ESG Explained

ESG Explained
ESG is a generic term used by investors to refer to the factors that can affect a company’s ability to create long-term value. It also refers to intangible assets. ~ PRI Academy Definition of ESG
- Pollution
- Biodiversity Loss
- Climate Change
- Deforestation
- Resource Depletion
- Waste Management Environmental
- Human Rights
- Child Labour
- Product Safety
- Product Mis-selling
- Labour Standards
- Employee Relations S Social
- Accounting
- Board Composition
- Bribery & Corruption
- Executive Pay
- Tax Avoidance
- Shareholders’ Rights
- Corporate Governance
Reports & Statements



The 3 Pillars of Corporate Sustainability
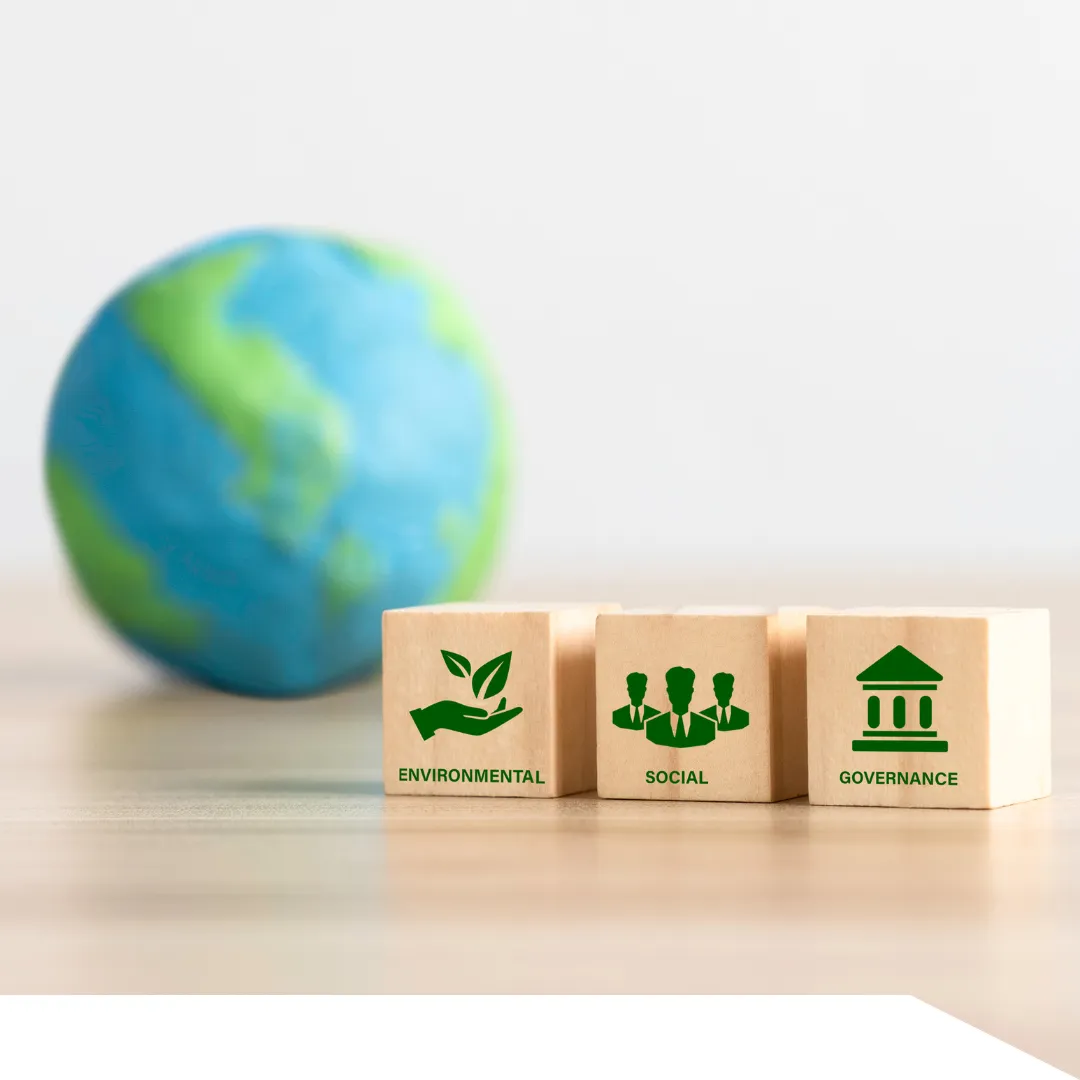

What Are the 3 Pillars of Corporate Sustainability?
Corporate sustainability has become a buzzword in companies big and small. Walmart Stores, Inc. (WMT), McDonald’s Corporation (MCD), and other large corporations have named sustainability as a key priority moving forward. Now other companies are under pressure to commit to finding sustainable ways to deliver their goods and services. At its essence, the term “corporate sustainability” refers to an approach to conducting business that creates sustainable, long-term shareholder, employee, consumer, and societal value by pursuing responsible environmental, social, and economic (or governance) strategies.
Key Takeaways
- Corporate sustainability is a growing concern among investors who seek not only economic profit but also social good.
- There are three pillars of corporate sustainability: the environmental, the socially responsible, and the economic.
- Companies can improve their environmental sustainability by, for example, reducing their carbon footprint or wasteful practices.
- The social responsibility pillar represents practices that benefit the company’s employees, consumers, and the wider community.
- The economic (or governance) pillar refers to maintaining honest and transparent accounting practices and regulatory compliance.

Neil Fletcher
Head of Operations & ESG















